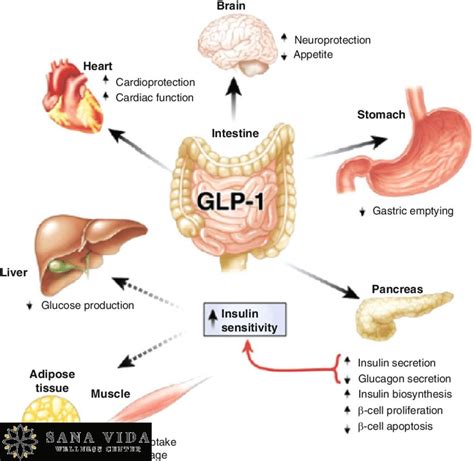
GLP-1’s Key Role: Understanding Its Impact on Health GLP-1, or
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1
, is a topic that’s gaining a lot of buzz, and for good reason! This isn’t just some complicated scientific term; it’s actually a
super important hormone
that plays a pivotal role in our overall health, especially when it comes to managing blood sugar, weight, and even protecting our hearts. Understanding
GLP-1’s key role
is crucial because it helps us grasp how our bodies regulate energy and how modern medicine is harnessing its power to combat major health challenges like Type 2 Diabetes and obesity. So, guys, let’s dive deep and explore the incredible impact of this unsung hero of our endocrine system. ## What Exactly is GLP-1? Your Body’s Amazing Helper Let’s kick things off by really understanding what
GLP-1
is. Imagine a tiny messenger in your body, a hormone that springs into action right after you eat. That’s essentially GLP-1! This powerful little peptide is primarily produced in the L-cells of your small intestine, and to a lesser extent, in your brain. It’s part of a group of hormones known as
incretins
, which are essentially chemical signals released by your gut when you consume food. The discovery of incretins, and specifically GLP-1, revolutionized our understanding of how the gut communicates with the pancreas and brain to regulate glucose. When food, especially carbohydrates and fats, enters your digestive system, it triggers these L-cells to release GLP-1 into your bloodstream. Its primary, and most widely recognized, function is its crucial role in glucose regulation. Think of it as a sophisticated alarm system that tells your body, “Hey, food’s coming, prepare for action!” But here’s the cool part: GLP-1 doesn’t just indiscriminately blast out insulin. Instead, it works in a
glucose-dependent
manner, meaning it only stimulates the pancreas to release insulin when blood sugar levels are high. This mechanism helps prevent dangerously low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), making it an incredibly smart and safe player in blood glucose control. Beyond this essential glucose management, GLP-1 is a
multifaceted hormone
with a broader impact than many realize. It doesn’t just stop at stimulating insulin; it also helps to suppress glucagon, another hormone that raises blood sugar, effectively working on both sides of the glucose equation. Furthermore, it influences how quickly food moves through your stomach, impacts your appetite, and even has protective effects on various organs. Its widespread influence across different bodily systems makes it a fascinating subject for medical research and a beacon of hope for improving metabolic health. Truly, understanding
GLP-1’s key role
in these fundamental processes is key to appreciating its significance in our health journey. ## The Core Functions of GLP-1: Beyond Just Blood Sugar When we talk about
GLP-1’s key role
, it’s easy to get caught up in just its blood sugar effects, but believe me, this hormone is doing so much more! It’s like a Swiss Army knife for your metabolism, boasting several critical functions that extend far beyond simple glucose control. Understanding these core functions helps us appreciate why it’s become such a valuable target in modern medicine and why maintaining healthy GLP-1 activity is paramount for overall well-being. ### Insulin Secretion and Glucose Control: A Dynamic Duo First up, let’s talk about the OG function: its direct impact on
insulin secretion
and overall
glucose control
. When you eat, and your blood sugar starts to rise, your gut’s L-cells release
GLP-1
. This powerful hormone then signals your pancreas, specifically the beta cells, to ramp up insulin production and release. But here’s the genius part, guys: this stimulation is entirely
glucose-dependent
. What does that mean? It means GLP-1 only prompts insulin release when your blood sugar is elevated. If your blood sugar is already at a normal level, GLP-1’s effect on insulin secretion significantly diminishes, thus preventing the risk of hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar. This intelligent, built-in safety mechanism is a major reason why GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are considered safer and more effective for managing Type 2 Diabetes compared to some older medications that can cause severe sugar drops. In addition to boosting insulin, GLP-1 also has another critical role in glucose regulation: it
suppresses glucagon secretion
. Glucagon is a hormone produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas that essentially does the opposite of insulin – it raises blood sugar by telling your liver to release stored glucose. By putting a brake on glucagon, GLP-1 ensures that your liver isn’t needlessly dumping glucose into your bloodstream, especially after a meal when you want blood sugar to go down. This double-whammy effect – increasing insulin and decreasing glucagon – makes GLP-1 an incredibly potent and effective regulator of blood glucose, helping to keep those post-meal sugar spikes in check and maintain overall glycemic stability. It’s a truly dynamic duo working tirelessly to keep your energy levels balanced. ### Slowing Gastric Emptying: Feeling Fuller, Longer Next on the list of
GLP-1’s key role
is its fascinating ability to
slow down gastric emptying
. Now, what exactly is gastric emptying? It’s simply the process by which food moves from your stomach into your small intestine. Think of it like a controlled release system. When GLP-1 is active, it puts the brakes on this process, making your stomach empty its contents at a much slower pace. Why is this important, you ask? Well, for a couple of big reasons! First, by slowing down the transit of food, it means that the glucose from your meal is absorbed into your bloodstream more gradually. This avoids those sudden, sharp spikes in blood sugar that can be particularly problematic for individuals with insulin resistance or Type 2 Diabetes. Instead, you get a smoother, more sustained release of energy, which is much easier for your body to manage. Second, and this is where it really helps with weight management,
slowing gastric emptying
contributes significantly to feelings of
satiety
. When food stays in your stomach longer, you naturally feel fuller for a longer period. This prolonged sensation of fullness helps to reduce overall food intake because you’re less likely to reach for snacks or overeat at your next meal. Imagine feeling satisfied and not constantly battling hunger pangs – that’s a huge win for anyone trying to manage their weight or simply avoid mindless eating. This mechanism is one of the primary ways that medications mimicking GLP-1 help people achieve substantial weight loss, by making them feel satisfied with smaller portions and less frequent eating. It’s a natural and effective way to manage calorie intake without feeling deprived, truly underscoring the powerful impact of
GLP-1
on our eating habits and digestive comfort. ### Appetite Regulation and Weight Management: Your Brain’s Best Friend Moving on, let’s talk about perhaps one of the most exciting aspects of
GLP-1’s key role
: its profound influence on
appetite regulation and weight management
. This hormone isn’t just working in your gut and pancreas; it’s also sending direct signals to your brain, specifically to areas like the hypothalamus, which is the command center for hunger and satiety. When GLP-1 levels are high, it essentially tells your brain, “Hey, we’ve had enough food, you can switch off the hunger signals!” This results in a significant
reduction in appetite
and a powerful increase in feelings of
fullness and satisfaction
. People often describe feeling less

